Urticaria (蕁麻疹) - Explained by Dr. Yeung Ho Hong (楊浩康)
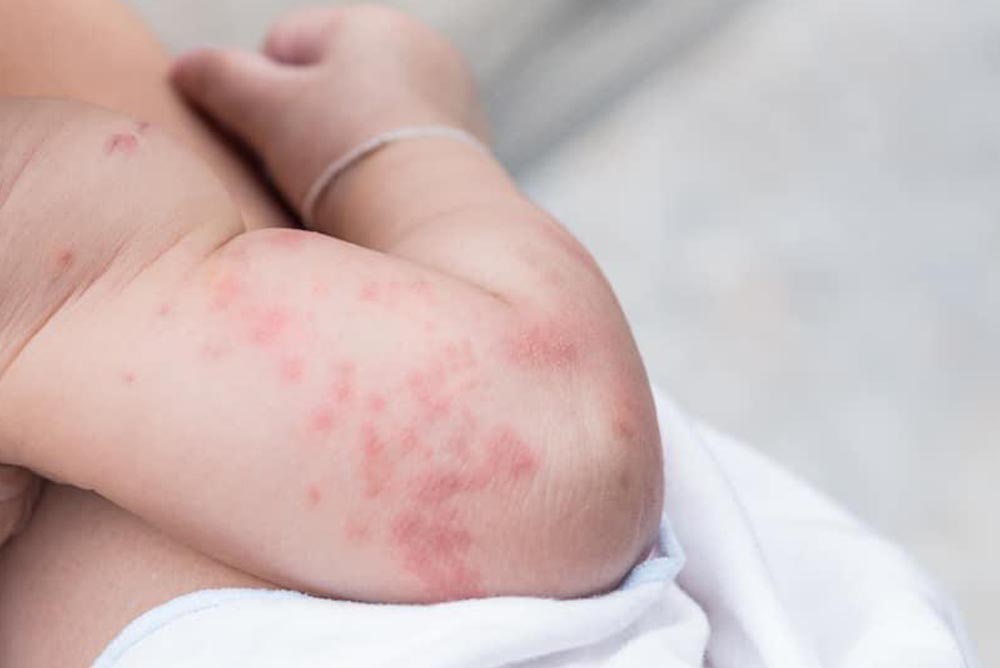
Urticaria (蕁麻疹), commonly known as hives, is a prevalent skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and raised welts on the skin that vary in size and shape. This condition can affect individuals of any age and may be acute or chronic, lasting from a few hours to several weeks. While urticaria is typically not life-threatening, it can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life, causing discomfort and distress.
The most common cause of urticaria is an allergic reaction to a substance or medication. Other potential triggers include stress, infections, exposure to hot or cold environments, and physical pressure on the skin. In some cases, the cause of urticaria may remain unknown.
Symptoms of urticaria can vary from person to person, with differences in severity and duration. The most common symptoms include red or pink rashes, skin swelling, itching, and a burning or stinging sensation. In severe cases, urticaria may lead to difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, and anaphylaxis—a life-threatening allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis of urticaria is typically based on a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. Blood tests or skin tests may also be conducted to help identify the underlying cause of the condition. Treatment for urticaria involves identifying and avoiding triggers, as well as using medications to relieve symptoms. Antihistamines (抗組織胺藥物) are the most commonly prescribed medications for urticaria. They work by blocking the release of histamine to alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, oral or injected corticosteroids (類固醇) may be used to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. In certain situations, other treatments such as phototherapy or immunosuppressive drugs may also be employed.
Preventing urticaria can be challenging, but avoiding known triggers and adopting stress-reduction measures can help prevent outbreaks. Maintaining good skin hygiene and avoiding tight clothing may also contribute to preventing the onset of urticaria.
In summary, urticaria is a common skin condition that can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. Through proper diagnosis, targeted treatment, and preventive strategies, its impact can be effectively managed. Consulting a professional physician for personalized guidance is essential to ensure optimal care and symptom control.
