What Topical Creams Are Available for Treating Eczema? - Explained by Dr. Yeung Ho Hong (楊浩康)
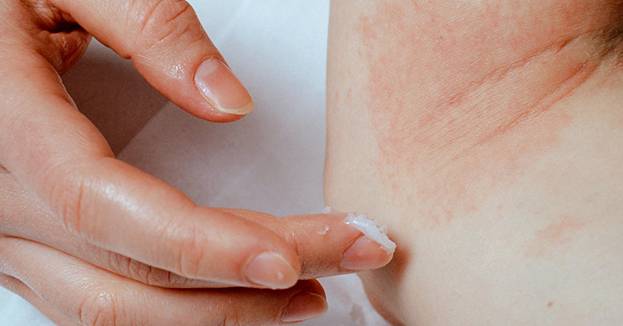
Good skincare is a critical component of eczema treatment. For mild cases, simply adjusting lifestyle habits and using gentle skincare products can effectively manage symptoms. However, when the condition becomes more severe, medication is often necessary in addition to daily care to improve skin condition, reduce inflammation, alleviate itching, and enhance the patient’s quality of life. This article will detail the commonly used topical creams for eczema treatment, including corticosteroids, non-steroidal creams, antibiotic creams, and the newer phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitors (磷酸雙酯酶4抑制劑), providing a comprehensive understanding of treatment options.
Topical creams for eczema treatment can be broadly categorized into four types: The first is corticosteroid creams (皮質類固醇藥膏), which offer potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects and are a primary choice for moderate to severe eczema; the second is non-steroidal creams, which provide significant anti-inflammatory benefits without causing skin thinning; the third is antibiotic creams (抗生素藥膏), used to treat eczema complicated by bacterial infections; and the fourth is the newer phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitors, which effectively and safely address mild to moderate atopic dermatitis.
Corticosteroid creams stand out for their remarkable anti-inflammatory effects, particularly during acute eczema flare-ups. Doctors typically select the strength of the cream based on the patient’s age, the extent of the lesions, and the specific area affected. For instance, low- or medium-potency formulations are often chosen for the face and thinner skin areas, while higher-potency options may be used on thicker skin, such as the hands or elbows. However, caution is essential when using corticosteroid creams: prolonged or excessive use can lead to side effects like skin thinning, telangiectasia (visible blood vessels), and stretch marks. Adhering strictly to a physician’s instructions is key to avoiding adverse reactions.
For patients with mild to moderate eczema, topical calcineurin inhibitor creams (鈣調神經磷酸酶抑制劑藥膏) are an excellent alternative. These creams offer anti-inflammatory benefits and are particularly suitable for patients over two years old. They reduce inflammation and itching without causing skin atrophy, unlike corticosteroids, making them ideal for long-term treatment on the face or other sensitive areas. Due to their higher safety profile, an increasing number of patients are opting for this treatment under medical guidance to achieve sustained symptom control.
Additionally, when eczema patients experience skin breaks or infections, antibiotic creams become particularly important. In cases where eczema is accompanied by bacterial infection, topical antibiotics can effectively suppress pathogen proliferation, prevent the spread of infection, and promote wound healing. The choice of antibiotic cream depends on the infection’s nature, and physicians guide patients on proper use to avoid issues like antibiotic resistance.
In recent years, phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitors have gained attention as a novel topical treatment. Multiple clinical studies highlight their efficacy and safety in treating mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. PDE4 inhibitors effectively reduce localized skin inflammation and itching, offering a promising option for patients who respond poorly to traditional treatments.
Overall, the variety of topical creams for eczema treatment—from corticosteroids to non-steroidal options, antibiotics, and the newer PDE4 inhibitors—each come with unique mechanisms of action and indications. The choice of cream depends on factors such as the patient’s age, severity of the condition, affected skin area, and presence of infection. In clinical practice, doctors often employ a combination of medications alongside proper skincare and lifestyle adjustments to achieve optimal outcomes. Given the chronic and recurrent nature of this skin condition, patients should work closely with a professional physician, adjusting treatment plans as needed based on symptom changes, to alleviate symptoms, improve skin health, and enhance quality of life.
