What is Molluscum Contagiosum (Commonly Known as Pearl Warts)? - Explained by Dr. Yeung Ho Hong
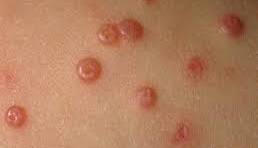
Molluscum contagiosum, popularly called "pearl warts," is a skin infection caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus, a poxvirus. Common in children, it can also affect teens and adults. It spreads through direct or indirect contact—e.g., skin-to-skin during play, or sharing toys, towels, or personal items. Children, with less mature immune systems, are more susceptible, while adults with weakened immunity or skin breaks may also contract it.
Once infected, small, smooth, flesh-colored bumps appear on the skin, typically round or oval, resembling tiny pearls—hence "pearl warts." These lesions, a few millimeters wide, often have a central dimple or pit, a hallmark feature. They frequently occur in clusters or scattered across the arms, trunk, legs, or face. Most patients feel minimal discomfort, but scratching can damage skin or cause secondary bacterial infections, triggering inflammation.
Transmission occurs via direct skin contact or indirectly. Scratching or rubbing the warts spreads the virus via hands to other areas. Sharing items like towels, bedding, clothes, or toys also facilitates spread. Good personal and household hygiene is crucial—parents should teach kids to avoid scratching lesions, wash hands frequently, and disinfect contaminated objects to curb transmission risk.
In most cases, molluscum contagiosum is self-limiting, resolving in months as immunity strengthens, even without treatment. However, for extensive, persistent, or psychologically distressing cases, treatment is advised. Common methods include topical salicylic acid (‘水楊酸’) to soften and remove warts via keratin dissolution; cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy infected cells; laser therapy for precise lesion removal; and, in some cases, surgical excision. Doctors tailor treatment based on age, lesion count, and location for optimal results with minimal side effects.
In summary, molluscum contagiosum is a common, contagious skin infection from a poxvirus, causing small, smooth bumps, mainly in children and some adults. Though often self-resolving, prolonged or cosmetically bothersome cases warrant treatments like salicylic acid, cryotherapy, laser, or surgery. Maintaining hygiene and avoiding shared items prevent spread. With proper care and treatment, most patients recover quickly, restoring healthy, confident skin.
